Have you ever tried jumping into the stock market and buying a stock you're excited about, but while you periodically check in on it, you don't have time to follow it around like a puppy? You turn around for a second, and that puppy has eaten your couch - or, in this metaphor, lost you a lot of money on a trade. For this reason, the stock market has a feature called stop losses, which allows for better risk management. These stop losses are a powerful tool that can help traders reduce risk, protect their capital, and improve their overall trading performance.
What is a stop Loss?
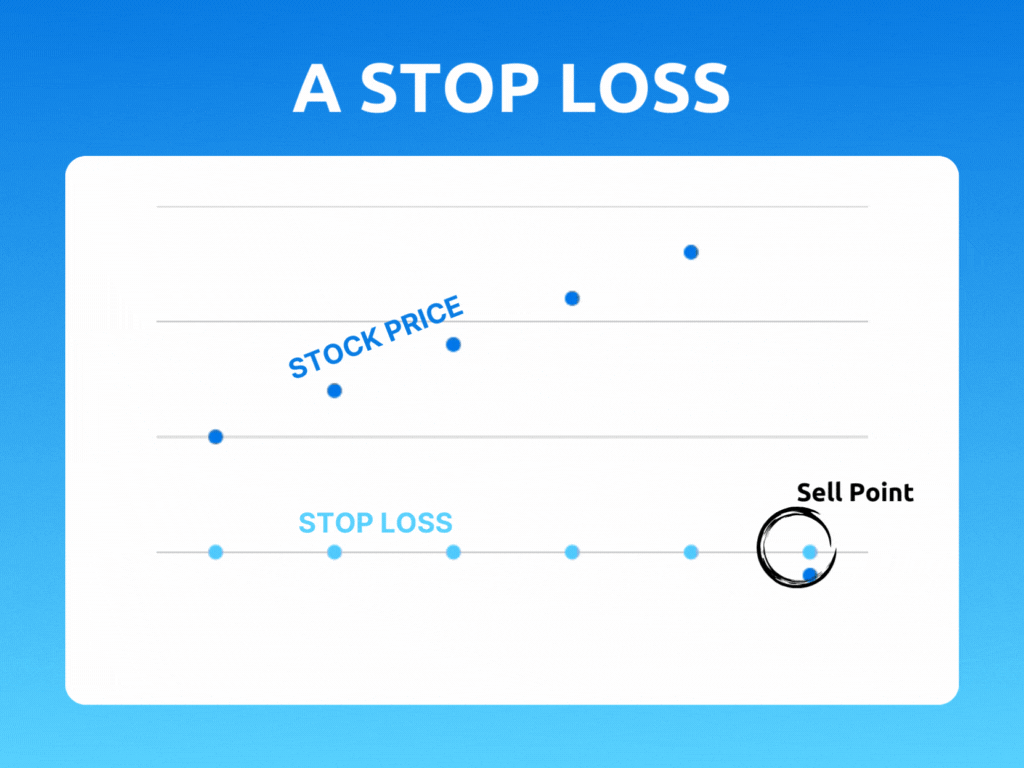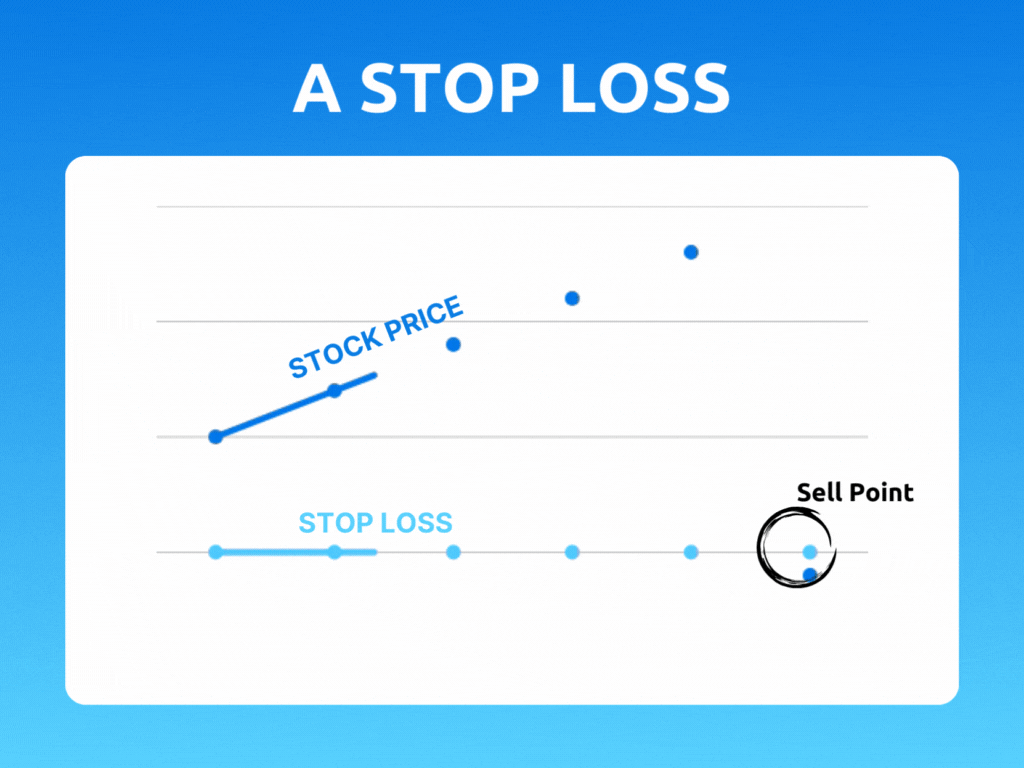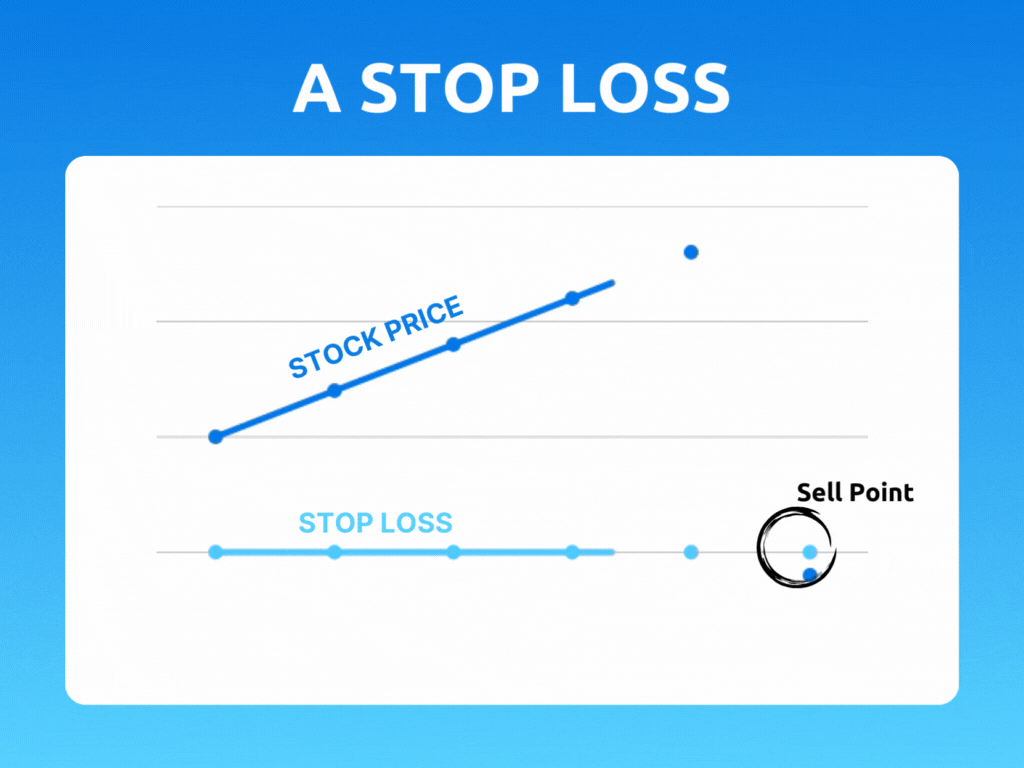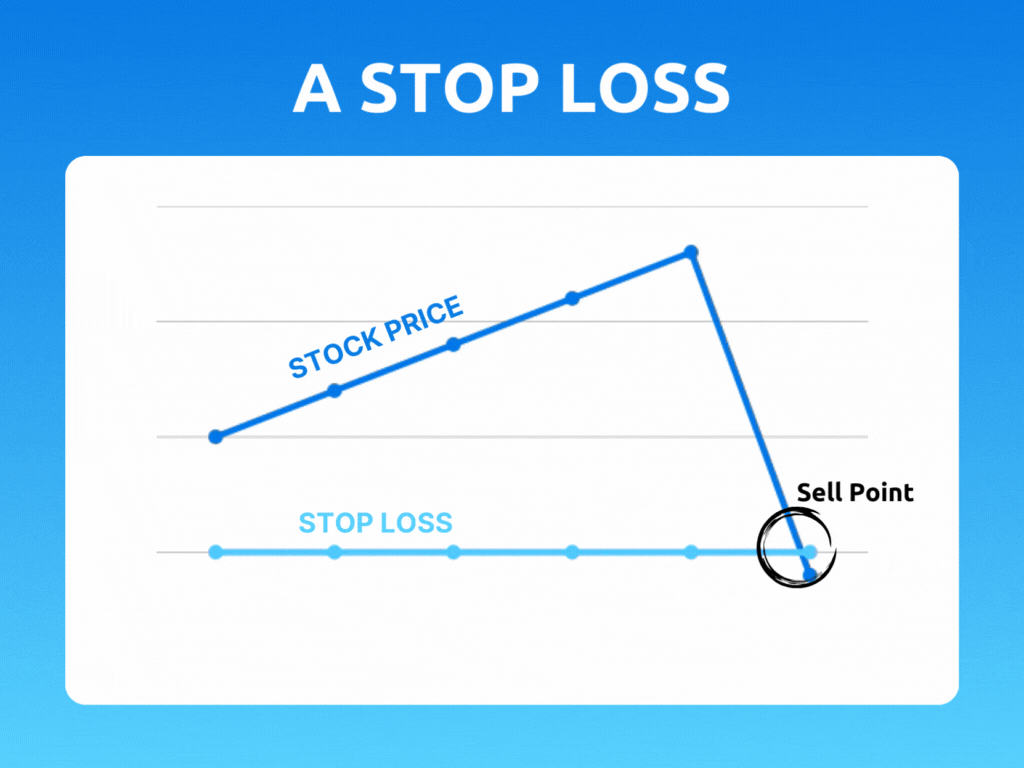
A stop loss is a predetermined point at which a trader will exit a position to limit their losses. It is essentially a safety net that helps traders manage risk by automatically closing out a trade if the price moves against them beyond a certain point. This point is set by the trader, and it can be adjusted based on their risk tolerance and trading strategy.
For example, let’s say a trader buys a stock at $50 and sets a stop loss at $45. If the price of the stock drops to $45, the stop loss will be triggered, and the trader’s position will be automatically closed out. This means that the trader will only lose $5 per share, rather than potentially losing much more if they had held on to the position.
What's a Trailing Stop?
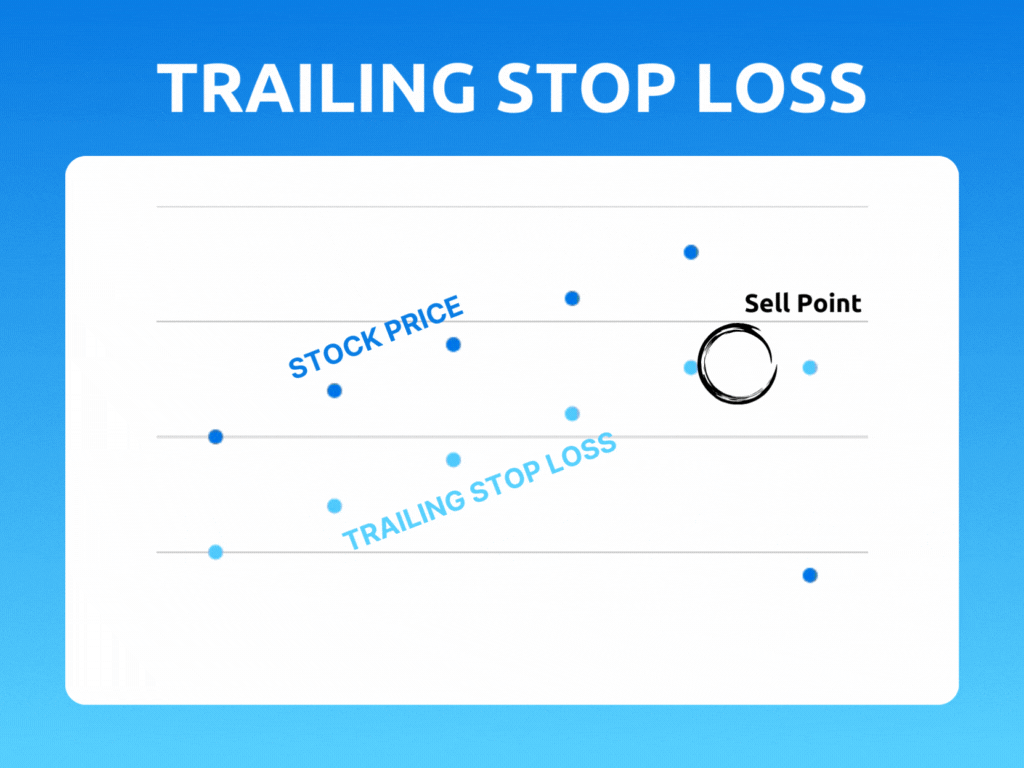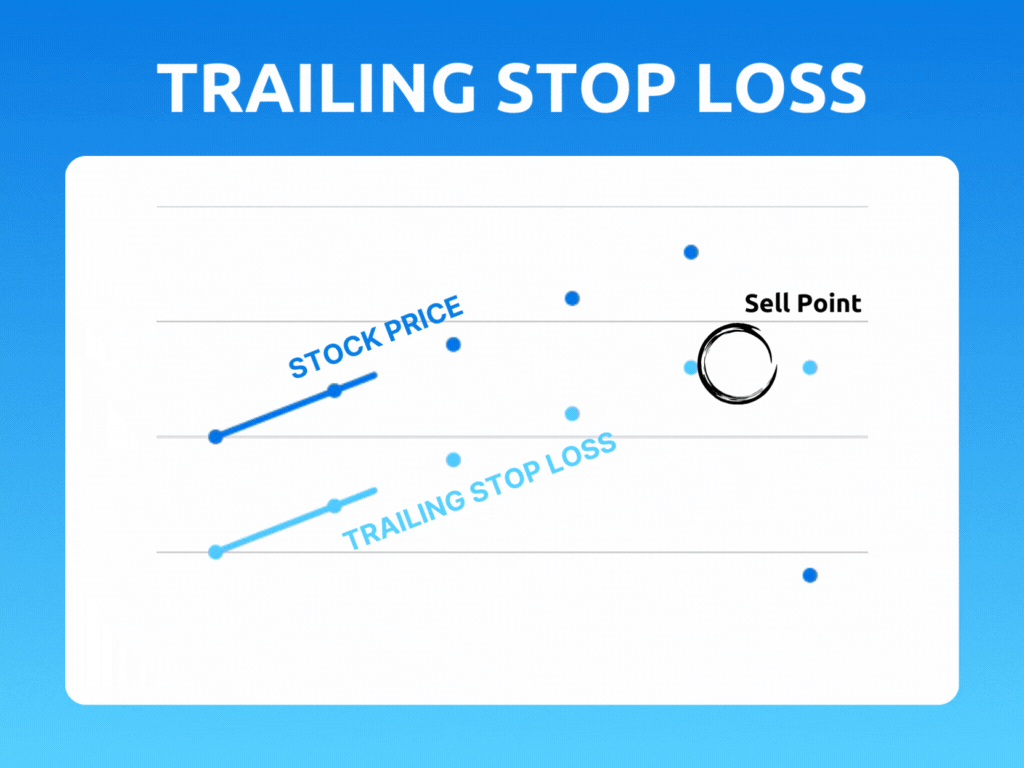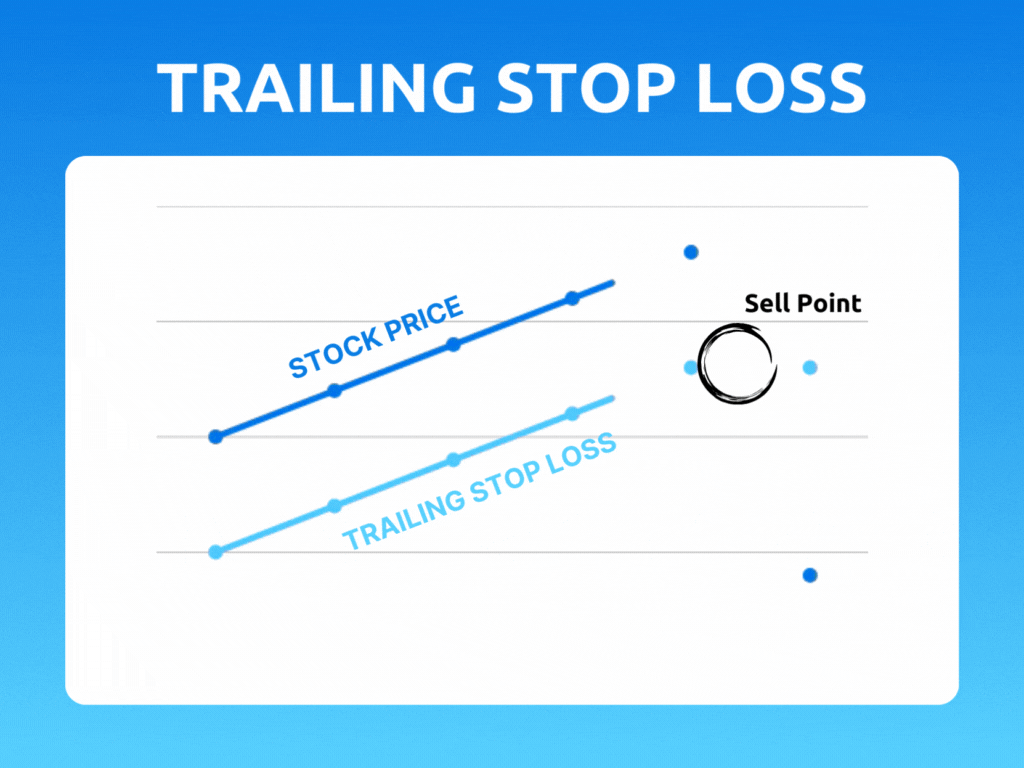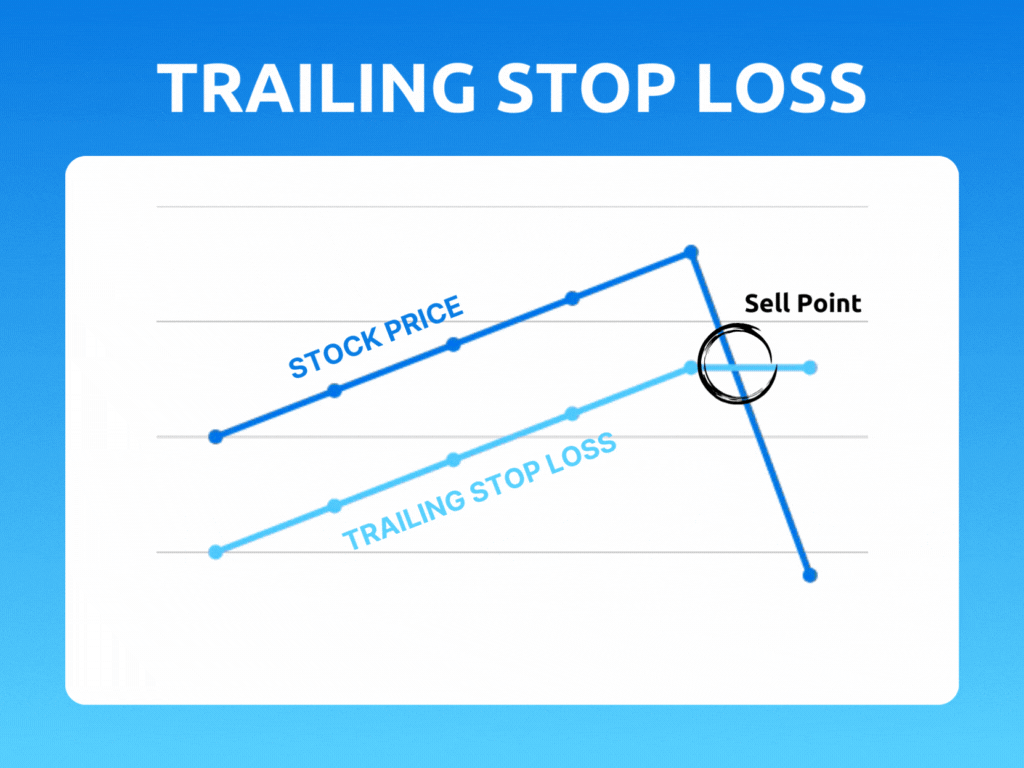
A trailing stop is an order type designed to lock in profits or limit losses as a trade moves favorably. Trailing stops only move if the price moves favorably.
As the stock price rises, the stop price rises by the trail amount. If the stock price drops, the stop loss price doesn't change, and a stop order is submitted when the stop price is hit.
As the stock price moves above the initial bid, the trigger price is reset to the new high minus the trailing amount. If the price stays the same or falls from the initial bid or highest subsequent high, the trailing stop maintains its existing trigger price.
Let's say you bought a stock at $50 per share and set a trailing stop of $5 per share. If the stock price rises to $55 per share, the stop price will be also be adjusted to $50 per share. If the stock price continues to rise to $100 per share, the stop price will be adjusted to $95 per share.
However, if the stock price starts to fall, the stop price will remain at $95 per share. If the stock price drops past $95 per share, the stop loss order will be triggered, and your position will be closed out at that price.
Why Use Stop Losses?
1
Reducing Risk
Stop losses can help traders reduce their risk by limiting their potential losses. By setting a stop loss at a predetermined level, traders can control their risk and prevent large losses.
2
Protecting Capital
Capital preservation is key in trading. By using stop losses, traders can protect their capital and avoid losing large amounts of money on a single trade.
3
Improved Performance
Stop losses can help traders improve their overall trading performance by minimizing losses and allowing them to stay in profitable trades for longer.
4
Emotional Control
Emotions can be a major hindrance to successful trading. By using stop losses, traders can remove emotions from their trading decisions and stick to their predetermined exit point.
The financial sector includes banks, fintech companies, loan providers, and insurance companies. Its primary function is to manage and distribute money, both for customers and corporations. The sector plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall stability of the financial system and ensuring efficient allocation of funds.